External DNS integration¶
The integration with an external DNS system is done via an extension which is invoked if certain buttons or API calls are done in the user interface:
As with all extensions, the DNS extension calls will originate on or be executed from the Site Controller. This will:
Create and delete A, AAAA (for IPv6) and PTR records for server instances when they get deployed and deleted from infrastructures
Create and delete A, AAAA (for IPv6) and PTR records for servers when registered and deleted
Create and delete A, AAAA (for IPv6) and PTR records for switches when registered and deleted
For this to work the following conditions must be met:
The Ansible Runner microservice must be running on the site controller
The DNS extension must be installed
The Ansible bundle capable of talking to the underlying DNS service must be uploaded to the repository
MetalSoft provides a sample PowerDNS DNS service in the Site Controller and the associated sample extensions.
Enabling the sample Power DNS service on the Site Controller¶
MetalSoft provides a sample DNS service that leverages PowerDNS to demonstrate how to integrate with other systems and to be used in POC Envs. The sample dns service is disabled by default. To enable it follow the following instructions on the Site Controller;
Create a directory
mkdir -p /opt/metalsoft/pdns
Add the following to
/opt/metalsoft/agents/docker-compose.yaml
pdns-auth-recursor:
container_name: pdns-auth-recursor
network_mode: host
hostname: pdns-auth-recursor
image: registry.metalsoft.dev/sc/sc-pdns-auth-recursor:develop
restart: always
environment:
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /opt/metalsoft/pdns:/appdata
Bring everything up
cd /opt/metalsoft/agents
docker compose up -d
Installing the DNS MetalSoft extension¶
Clone the sample DNS workflow repository.
git clone https://github.com/metalsoft-io/metalsoft-extensions
cd metalsoft-extensions
cd dns-workflow
Update the references to the DNS service in the ansible bundle
Edit the ansible/roles/powerdns/defaults/main.yml file and update the following variables:
powerdns_api_host: "localhost"
powerdns_api_port: 8081
powerdns_api_key: "your-api-key"
The powerdns_api_host is the IP address of the Site Controller. The default powerdns_api_port is 8081.
To retrieve the powerdns_api_key key from the image run the following command from the Site Controller:
docker exec -it pdns-auth-recursor grep api-key /etc/powerdns/pdns.conf | awk -F '=' '{print $2}'
Zip and upload the ansible script to the repository
Create a zip file of the contents of the ansible directory
cd ansible
zip ../power_dns.zip deploy_dns_flexible.yaml roles
cd ..
Upload the ansible bundle zip to an http server reachable by the Global Controller such as:
https://repo.metalsoft.io/.extensions_ms/workflows/power_dns.zip.Update the ansible bundle
URLin thepdns-workflow-example/extension.jsonfile in theassetssection to match the URL where the bundle will be accessible.
"assets": [
{
"label": "power-dns-configuration",
"name": "power-dns-configuration",
"assetType": "Bundle",
"url": "https://repo.metalsoft.io/.extensions_ms/workflows/power_dns.zip"
}
],
Install the extension using the CLI:
metalcloud-cli extension create test-dns workflow "test dns workflow" --definition-source pdns-workflow-full-example.json --format json
Publish the extension
metalcloud-cli extension publish 1
metalcloud-cli extension make-public 1
Go to Global Configuration > DNS and ensure that the configuration is correct for your environment, especially the NS.
Go to Sites > Site and ensure that the DNS zone that is selected in the drop-down is the one configured in the Global Configurations
Enable the Ansible Runner capability on the site controller¶
MetalSoft provides a component that executes Ansible scripts in the Site Controller but that is not enabled by default.
To enable, perform the following on the Site Controller:
Create a directory to store the transient Ansible jobs
mkdir -p /opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs
Enable the Ansible Runner docker container Edit the
docker-compose.yamlfile and add the Ansible runner pod and uncomment the following entries in theservicessection:
ansible-runner:
container_name: ansible-runner
network_mode: host
hostname: ansible-runner-qa02-os10-b9425
image: registry.metalsoft.dev/sc/sc-ansible-playbook-runner:openshift
restart: always
environment:
- TZ=Etc/UTC
- ANSIBLE_RUNNER=enabled
- ANSIBLE_RUNNER_HOME=/opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs
- ANSIBLE_RUNNER_ARCHIVES_FOLDER=/opt/metalsoft/ansible-archives
volumes:
- /opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs:/opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs
- /opt/metalsoft/nfs-storage:/iso
And in the same file, but the ms-agent section:
environment:
- ANSIBLE_RUNNER=enabled
volumes:
- /opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs:/opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs
Enable the Ansible Runner Capability
environment:
- ANSIBLE_RUNNER=enabled
volumes:
- /opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs:/opt/metalsoft/ansible-jobs
Power on the Ansible Runner and the PowerDNS service (as well as the other docker contaienrs)
docker compose down
docker compose up
Using the DNS extension to create DNS records for servers and endpoints¶
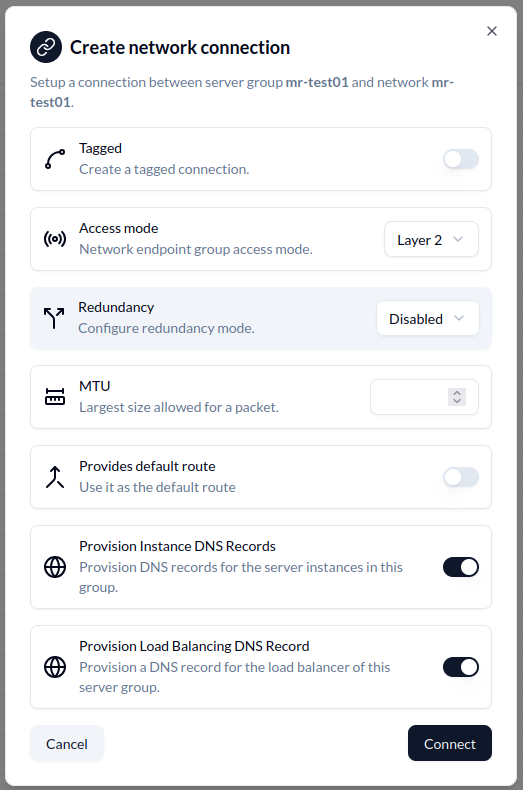
To create the records in the DNS via the extension connect an endpoint to a network. The DNS options are available under Provision Instance DNS Records and Provision Load Balancing DNS Record.
The first option will create records for each server, endpoint or VM attached to the network whereas the last will create a single DNS record with CNAME entries for all.
Customizing the DNS record that gets created¶
The default records look like this:
ID: 26
Domain: eveng-qa02.metalcloud.io
Name: instance-3878.eveng-qa02.metalcloud.io
Type: A
Content: 10.255.146.232
TTL: 3600 ✓
If the hostname field of the instance object is not set, the system uses instance-${instance_id} as a prefix Thus to customize the entry that gets created edit the hostname field of the server instance object (not server instance group).
More details on the behavior of the extension¶
Consult the Extension Readme for more details on the behaviour of the extension and how to modify it to suit your needs.
Ports open¶
In addition to the normal Site Controller ports, this component adds the following port:
port 53 -> the DNS recursor will listen on this port for DNS requests.
Enabling DNS records on servers and switches¶
The mechanism is capable of creating DNS records for the servers’s BMCs interfaces as well. This is useful in Ipv6-only environments.
To enable it append the two tasks to the extension definition:
{
"stage": "serverCreateDNS",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "create-dns-and-ptr-records-for-server",
"taskType": "ExtensionTaskAnsible",
"options": {
"asset": "power-dns-configuration",
"playbook": "deploy_dns_flexible.yaml"
}
}
]
},
{
"stage": "serverDeleteDNS",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "delete-dns-and-ptr-records-for-server",
"taskType": "ExtensionTaskAnsible",
"options": {
"asset": "power-dns-configuration",
"playbook": "deploy_dns_flexible.yaml"
}
}
]
}
A complete example can be found on github.