Server lifecycle¶
The following are the states as they are defined by MetalSoft:
Server states¶
Available
A server is healthy and ready to be used in a new provisioning operation. An admin will manually change a server to available from unavailable once the configuration of the server has been checked (Disks and Switch Interfaces). The system can be set to automatically set the server to Available once the server has been registered by going to Sites, Site name, Configuration and tick Automatically set servers as available This is normally a manually set state.
Available_reserved
State available_reserved is automatically set on a server that is in the available state but is reserved under a subscription for a specific user. This is an automatically set state.
Used
A server is already used and cannot be used in a new provisioning process in the current state. A server cannot be manually changed to used and should not manually be changed to another state from used. This is an automatically set state.
Registering
When a new server is first added to the application, it will pass through a complex process so the system is aware of the servers hardware components, configuration etc. For this a live, lightweight and custom linux image is booted via the BMC and a series of scripts are run. This is an automatically set state.
Cleaning
A server under the cleaning state is in the middle of a de-provision operation. The same live linux image runs clean-up scripts during this stage, making the server ready for a new provisioning operation. This is an automatically set state.
Defective
When specific issues occur with a server or hardware faults are present, a server can be marked as defective, from the advanced page. When in defective state, a server cannot pass into the Used state. This is a manually set state.
Used_registering
A server is in the used_registering state when an already used server is passed through the registering process. Once the registration process completes, the server will re-enter used state. This is an automatically set state.
Decommissioned
The decommissioning state describes a server that has been removed from the application and cannot be used unless re-added again (going back through the first server cycle described below). This is an automatically set state.
Removed from Rack When a server is no longer required, but the administrator needs to keep audit data, the server should be changed to removed_from_rack. This is a manually set state.
Interact with the server states¶
All the servers in all their states, can be seen in the Server type utilization report page.
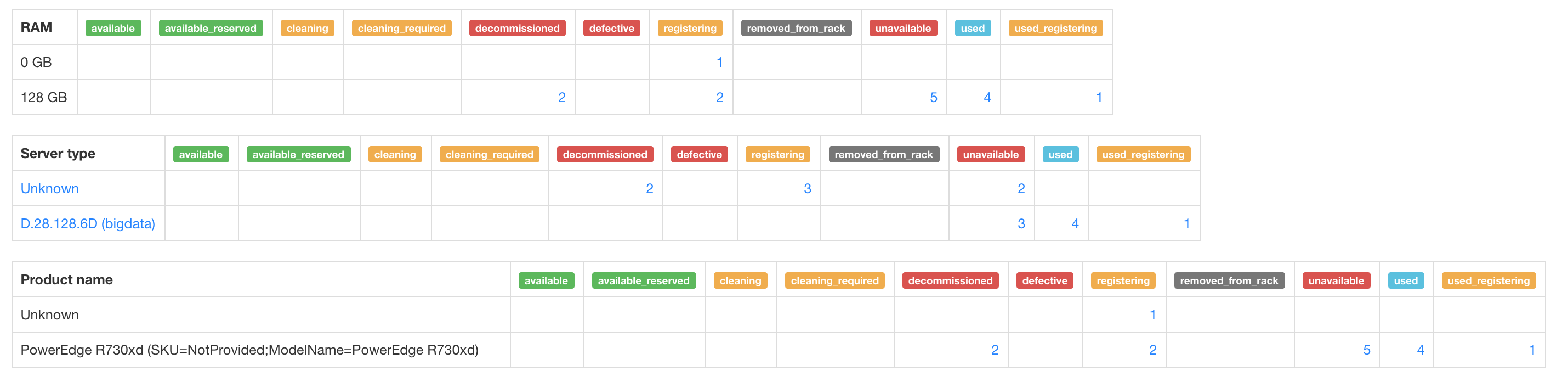
Administrators can interact with the server states. They can do so by accessing the Servers page, going to the Server status section and selecting the desired state. From here, the server can be moved into available, unavailable, defective or removed_from_rack You should not, in normal circumstances move a server to Used or from Used to another state unless the server is defective or decommissioned.
The registration and decommissioning processes can be triggered from the specific section.
Server cycles¶
1. Adding a server and using it
When a new server is first added into the application, it first passes through the registering process. If the registering processes succeeds, then it goes into the unavailable state. From here, it can be set manually in the available state or set to become automatically available. From here on, the server can be selected and used in a provision process.
2. Modifying and re-registering a used server
When modifications need to be done to a server in state, the re-register processes can be issued to an active server.
3. Releasing a server and using it again
The following diagram shows the states of a server from its release to its re-use.
4. Marking a server as defective
The process of marking a server as defective is manual. Once a server is diagnosed as unhealthy, the below can be selected to mark it as defective. Note that the server must not be in Used state when tagging it as defective.

During the server recovery, the Metadata section can be used to note down the fault, current status and other details.

After the server is repaired, it can be set to available again using the Available button.

The following diagram shows the states of a server from marking it as defective to setting it as available again and then being used.
Managing hardware failures and changes¶
During a servers life, there will be a need to replace components, or upgrade the server. For some changes, MetalSoft would need to be made aware of the changes so the server type can be presented correctly and the networking can perform as expected.
No Re-Registration required (but advised)¶
For the following types of replacement, nothing will need to be changed in MetalSoft:
Replace RAM same size as failed module
Replace Disk same size/model/type as failed module
(If the disk is replaced, we still strongly suggest the server is re-registered at some point so MetalSoft is aware of the serial number. This can be performed using Re-register, but will cause the server to be rebooted)Replace CPU same model/type as failed module
Network card changes¶
If the Nic needs to be replaced, then the server would need to be re-registered. How this is performed differs between if it is in Available/Unavailable or Used state:
Available - If the server is in Available state, then the server can just be changed to Unavailable state and then re-registered
Unavailable – If the server us in Unavailable state, then the server can just be re-registered
Used – If the server is in Used state, then you can still re-register. You do not need to change the state from Used, you will just need to click on re-register
Please be aware, this will cause a reboot of the serverIf the Nic is plugged into different ports on the switch, then the network configuration on the OS may need to be manually changed as MetalSoft does not have access to an installed OS.
BMC board/Motherboard changes¶
If the BMC board on a server (and, in some instances, the motherboard)which is in Used state is replaced, then we would strongly suggest the server is backed up, removed from the infrastructure, then the server status changed from Available to Unavailable and the server will need to be Decommissioned (from the Advanced tab) and then registered. Before decommissioning the server, please ensure you make a copy of the BMC IP address, user and password as well as the serial number.
Upgrading a server¶
If the desire is to upgrade a servers resources, then the server can not be used by any infrastructure (will need to be in available state) and then the server would need to be changed to Unavailable and re-registered. Once changed back to Available, the server will have a new server type which will indicate the new configuration.